4 Real Use Cases of AI Manga Translators Explained
Summary: AI manga translators are not just for reading. Discover 4 real ways to translate manga, read other languages, create content, and earn money legally.

Many people think manga translation is only needed when reading Japanese comics for fun.
In real situations, the need to translate manga comes from very different reasons. Some people have to work with raw manga pages and cannot afford to redraw them. Others want to read manga that has no official translation in their language. There are also creators who need to publish manga content for a global audience, as well as people who translate manga as part of their work.
In recent years, tools like an AI Manga Translator have become part of these workflows. This article looks at four real situations where manga translation is actually needed, and how these problems are commonly handled today.
How Scanlation Teams Translate Raw Manga Without Redrawing
When Raw Manga Must Be Translated
This situation usually happens in a few clear cases:
- Fast updates 📅
Popular series are released frequently, and waiting for official translations takes too long. - No foreign editions 🌍
Some manga are only published in Japanese, with no English or other language versions available. - Story-first reading 📖
Readers care more about the plot than polished, fully redrawn pages.
Real Constraints Scanlation Teams Face
In practice, scanlation teams work under strict limits:
- ❌ Not everyone understands Japanese
- 👥 Limited team members and time
- 🎨 Redrawing text bubbles takes too much effort
- 📄 Large numbers of pages per release
These constraints make traditional redraw-and-edit workflows hard to maintain.
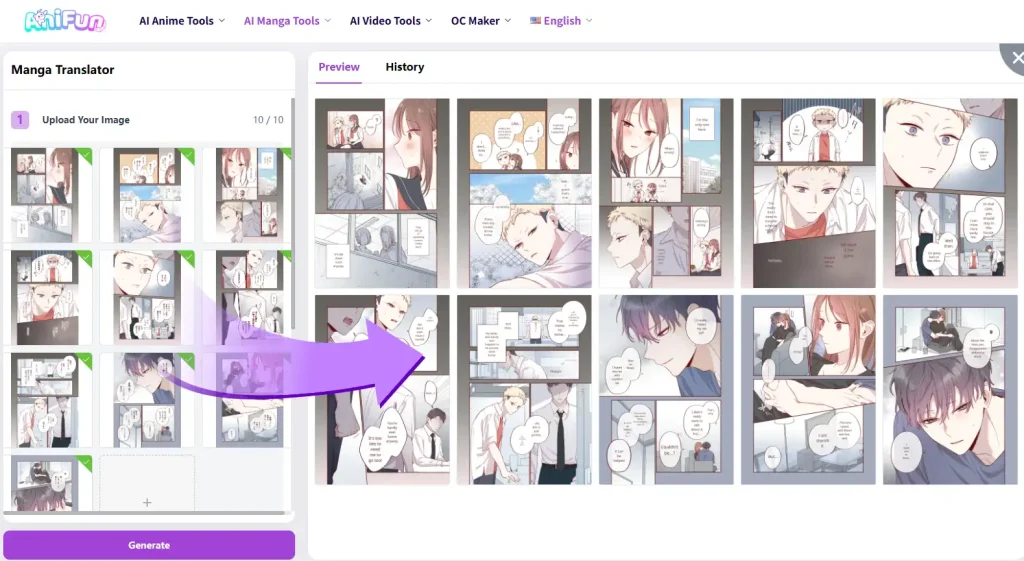
How an AI Manga Translator Fits This Workflow
An AI Manga Translator helps by focusing only on the text, not the artwork:
- Detects dialogue inside speech bubbles automatically
- Places translated text directly on the original page
- Adjusts text size and layout to fit the bubbles
- Processes multiple pages at once 🚀
How Global Manga Fans Use AI to Read Japanese and Other Languages
Why Regular Readers Still Need Manga Translation
Even casual manga fans run into translation issues:
- No official translations available
Many titles are never released outside Japan. - Niche or indie works 🧩
Small publishers and doujin works are often limited to one language. - Early access matters
Fans want to read new chapters as soon as they are released, not months later.
Problems With Traditional Reading Methods
Before AI tools, readers usually relied on workarounds:
- 🔍 Manually looking up dialogue line by line
- 🧠 Guessing meaning from partial translations
- ⏳ Constantly switching between apps or tabs
These methods interrupt reading flow and make it hard to stay immersed in the story.
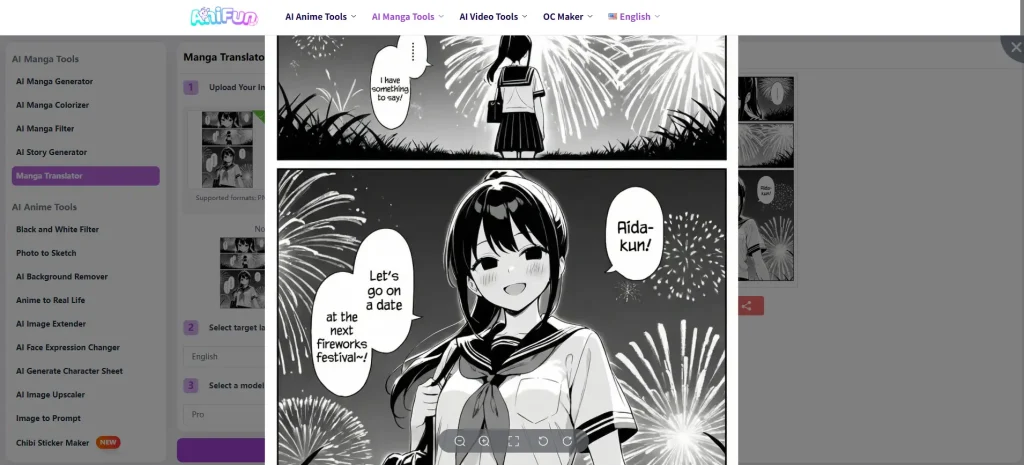
What the AI Manga Translator Reading Experience Feels Like
The Manga Translator changes the reading experience rather than the artwork itself:
- Supports over 130 languages 🌍
Readers can choose their preferred language instantly. - Reads directly on the original image
No text extraction, no file conversion. - No downloads required
Pages can be read online as-is. - Original artwork stays untouched
The layout, panels, and art style remain intact.
How Content Creators Produce Multilingual Manga Faster
The Real Multilingual Pressure Creators Face
As distribution becomes global, creators run into the same challenges:
- Global social platforms 🌍
Manga shared on X, Instagram, or other platforms reaches audiences in many languages. - High cost of repetition
Manually recreating the same page for each language wastes time and energy. - Short content cycles
Delays in translation often mean missed engagement opportunities.
Why Manually Extracting Text Doesn’t Scale
Traditional workflows depend on text extraction, but manga makes this difficult:
- 🧩 Text appears in irregular bubbles and shapes
- 📐 Dialogue placement varies across panels
- ❌ Manual extraction increases the risk of missing or incorrect lines
These issues slow production and introduce avoidable errors.
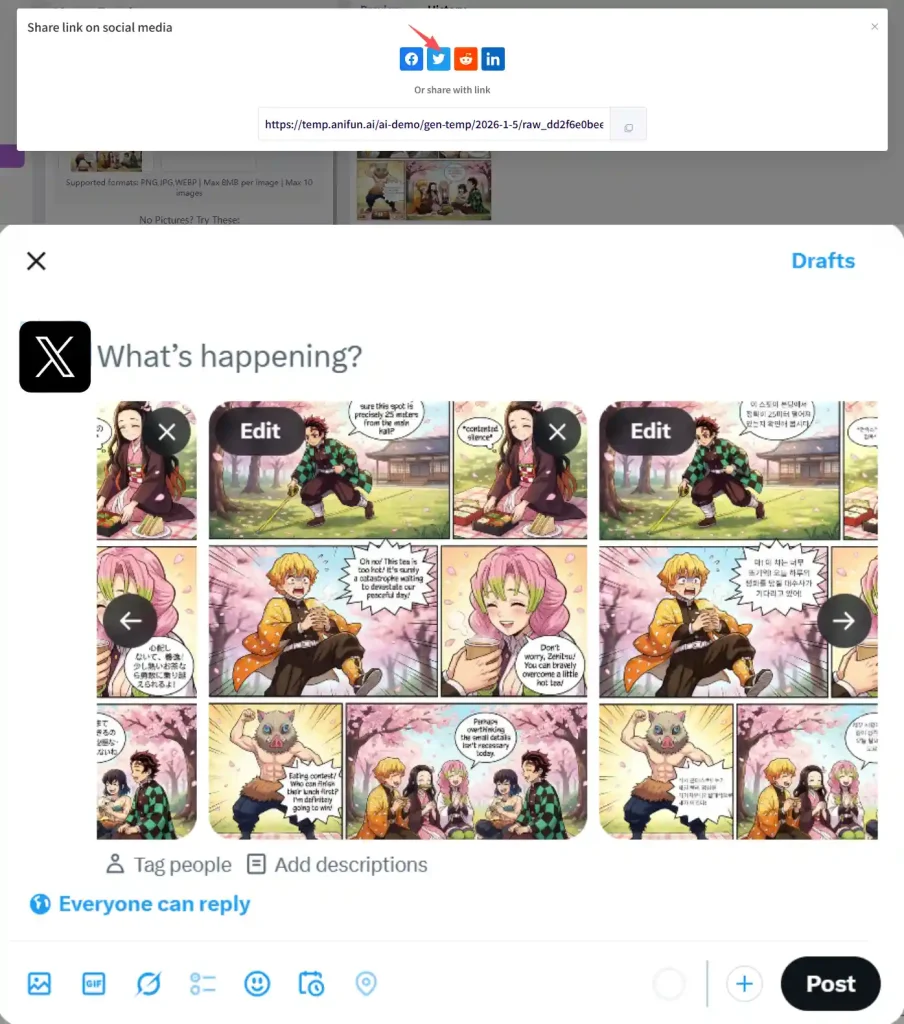
How Ready-to-Use Images Are Generated for Publishing
Instead of separating text and artwork, the translation happens directly on the page:
- The original image remains untouched
Speech bubbles, panels, and composition stay exactly the same. - Translated text fits naturally into the layout
Font size and spacing adjust automatically to match the bubble shape. - Images are ready to publish immediately
Pages can be downloaded or shared as final outputs, without extra editing 📤
How Manga Translation Can Become a Legal Income Stream (DLsite Example)
For translators and bilingual creators, manga translation can be more than a hobby. With the right platform and permissions, it becomes a legitimate way to earn income.
How the DLsite Translator Program Works
DLsite allows translated manga to be sold under a clear rights framework:
- Original creator authorization
Translations are published with permission from the rights holder. - Platform-managed distribution
DLsite handles hosting, sales, and payments. - Revenue sharing model
Income is split between the original creator, translator, and the platform.
This structure protects both creators and translators while enabling global distribution.
Why Translation Is a Low-Barrier Entry Point
- ✍️ No need to create original artwork
- 💰 Lower upfront cost
- ⏱ Faster turnaround per title
How Faster Translation Helps You Earn Sooner
- Translate pages without upfront tool costs A free workflow makes it easier to test ideas and build experience.
- Handle multiple pages efficiently Faster turnaround helps you release translations closer to the original launch.
- Submit ready-to-use images directly Final pages can be uploaded to platforms like DLsite without additional editing.
Conclusion
Manga translation today serves more than one purpose. It supports scanlation teams, helps readers access foreign-language titles, enables creators to publish globally, and provides a legitimate path for translators to monetize their work. Across all these use cases, the core needs remain the same: speed, accuracy, and respect for the original artwork.
By removing steps like manual text extraction and page redrawing, modern translation workflows make manga easier to translate, share, and publish across languages—without changing how it looks or reads.
